- On February 11, 2015, the United States filed a challenge in the WTO against China’s “Demonstration Bases-Common Service Platform” program that provides prohibited export subsidies to Chinese enterprises located in 179 industrial clusters throughout China known as “Demonstration Bases.”
- Each of these Demonstration Bases was comprised of enterprises from one of seven sectors: (1) textiles, apparel and footwear; (2) advanced materials and metals (including specialty steel, titanium and aluminum products); (3) light industry; (4) specialty chemicals; (5) medical products; (6) hardware and building materials; and (7) agriculture.
- The WTO established a panel in April 2015 to review this matter. Nonetheless, the parties continued to discuss how China could address U.S. concerns that China’s program provides export subsidies prohibited under WTO rules.
- To address the concerns raised by the United States, China agreed to take specific actions in a memorandum of understanding (MOU) signed on April 14, 2016 by China and the United States.
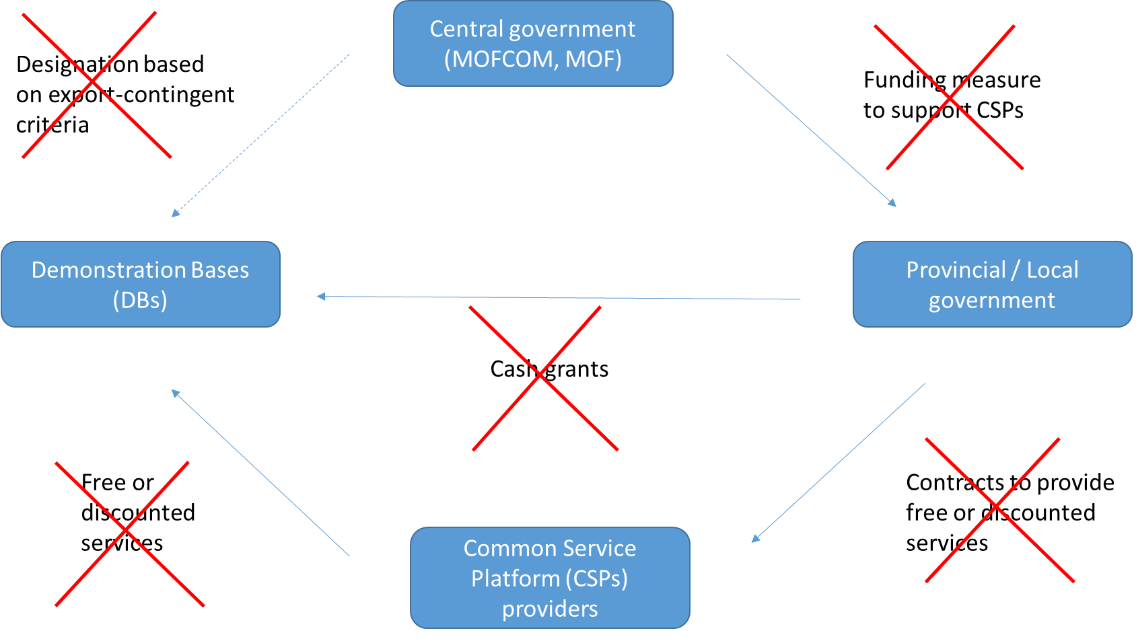
- In the MOU, China agreed to take the following actions with respect to the Demonstration Bases-Common Service Platform program:
- Defund the Common Service Platform (CSP) program by removing central government level funding;
- Terminate the preferential service agreements between sub-central governments and CSP providers, which had been the sources of free or discounted services provided to Demonstration Base enterprises;
- Prohibit CSP providers from continuing to provide free or discounted services to enterprises in export-contingent Demonstration Bases;
- Terminate sub-central government export-contingent cash grant measures;
- Eliminate any export-contingent criteria from the Demonstration Base designation process; and
- Re-evaluate all national and provincial level bases without the use of export-contingent criteria.
The following diagrams illustrate the actions that the MOU covers.
Prior to the MOU:
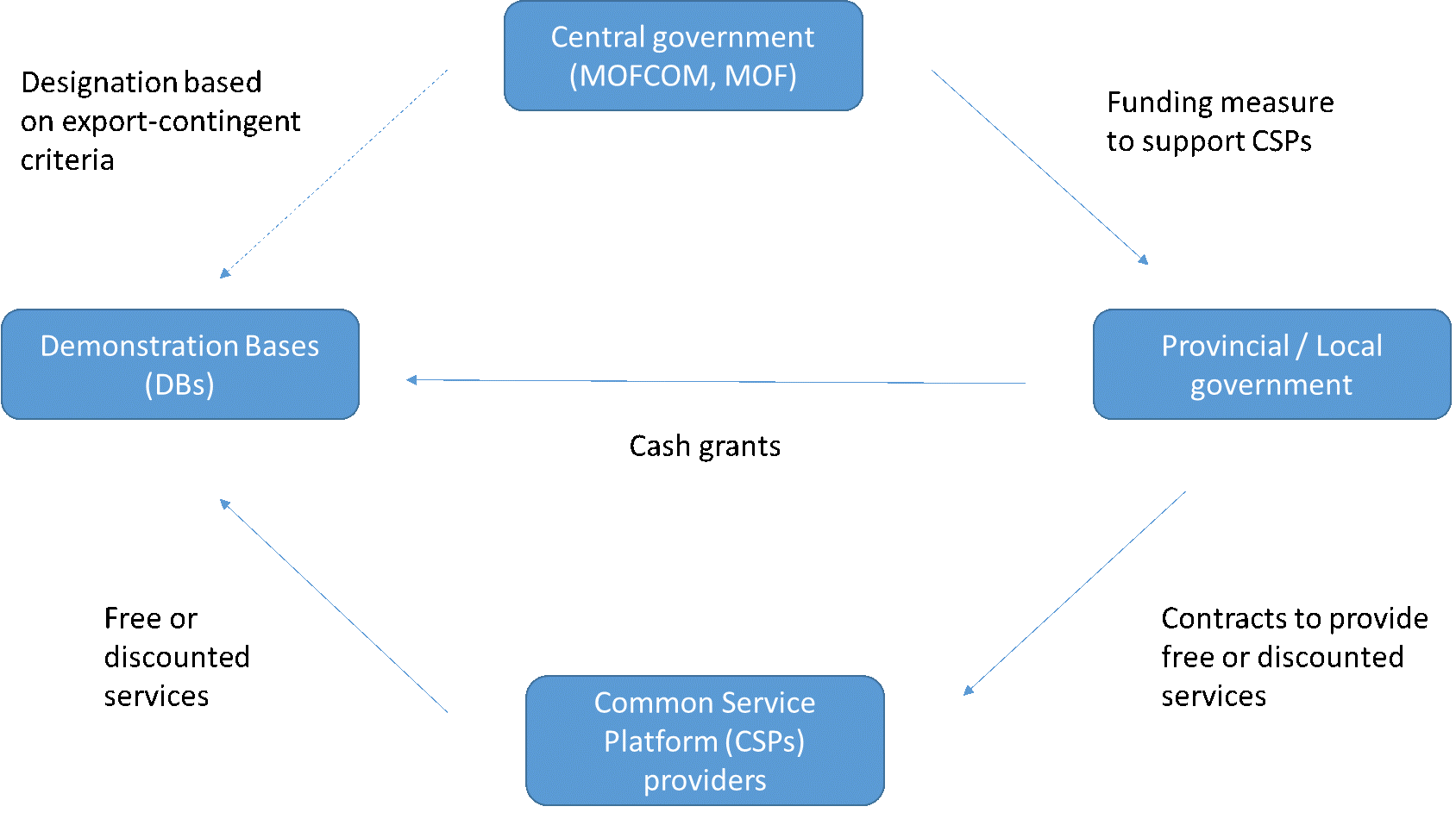
Following the MOU:
- The United States challenged 175 Chinese government legal instruments in the WTO panel request. Since then, China has terminated, amended, replaced, or allowed to expire all 175 instruments. Additionally, China has terminated, amended, replaced, or allowed to expire additional measures beyond those listed in the panel request.
- China has provided the United States with 136 measures it has issued to implement the terms of the memorandum of understanding. These measures affect the Demonstration Base-Common Service Platform program at the national level as well as in 29 of China’s largest industrial provinces and municipalities, including Guangdong, Shandong, Sichuan, Jiangsu, Beijing, and Shanghai.
- China’s Ministry of Commerce and Ministry of Finance have terminated all existing preferential service agreements between CSP service suppliers and local governments across the country.
- During the consultations, the United States emphasized concerns about the transparency of the program and the preferential service agreements. China has now disclosed more than six times as many preferential service agreements than what was publically available before the start of the consultations.
- Prior to the consultations, only two provinces had made any of their preferential service agreements available to the public. As a result of the U.S. action, China has disclosed information from more than 10 provinces and provincial-level municipalities, including measures terminating preferential service agreements from more than 50 cities and counties.
- China has agreed to exchange further information related to the future actions taken pursuant to the MOU signed today.